Leo I, Prince of Armenia
| Leo I Լևոն Ա | |
|---|---|
| Lord of Cilicia | |
| Lord of Armenian Cilicia | |
| Reign | 1129/1130–1137 |
| Predecessor | Constantine II |
| Successor | Thoros II (in 1144/45) |
| Born | 1080 |
| Died | February 14, 1140 (aged 59–60) Constantinople |
| Spouse | Beatrix (Beatrice) of Rethel |
| Issue | one/two unnamed daughter(s) (?) Constantine Thoros II Stephen Mleh I Roupen |
| House | Roupenians |
| Father | Constantine I |
| Mother | An unnamed great-granddaughter of Bardas Phokas |
Leo I[1] (Armenian: Լևոն Ա), also Levon I[2] or Leon I,[3] (unknown[citation needed] – Constantinople, February 14, 1140[citation needed]) was the fifth lord of Armenian Cilicia[2] (1129[2]/1130[1]-1137[1][2]).
He expanded his rule over the Cilician plains and even to the Mediterranean shores. In his time, relations between the Armenians and the Franks (the Crusaders), two former allies, were not always as courteous as before: a major cause of dissension between them was the ownership of the strongholds of the southern Amanus, and on the neighboring coasts of the Gulf of Alexandretta.[4]
Leo was captured after being invited to a meeting by the Byzantine Emperor John II Comnenus, who had sworn a false promise of peace.[5]
His early life
[edit]Leo's father was Constantine I, lord of Armenian Cilicia.[citation needed]
After the death of Constantine I, Leo's brother Thoros I became the ruler.[2] Sometime between 1100 and 1103,[citation needed] Leo married[2]
/Leo/ invited many famous warriors to join him, and allured them by great rewards. Forward in battle, he prepared himself, and often fought against the foreigners or infidels, took their forts and put all the inhabitants to the sword. He was the admiration of warriors, and the fear of foreigners or infidels, so that they called him the new Ashtahag.
— Vahram of Edessa: The Rhymed Chronicle of Armenia Minor[6]
His rule
[edit]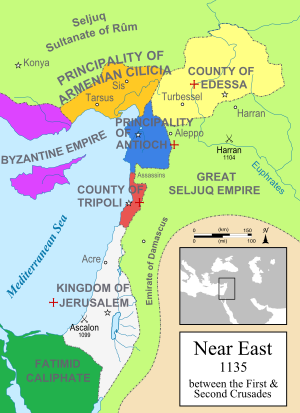
Other authors (e.g., Jacob G. Ghazarian, Vahan M. Kurkjian) suggest that Thoros I was directly succeeded by Leo.[2][3]
Conflicts with the Franks
[edit]Leo paid 60,000 gold pieces and gave his son as a hostage. An alliance was then formed against the Emperor John II Comnenus, who was then pressing his claims against Antioch as well as Cilicia.[7]
The (re-)occupation of Cilicia by the Byzantines
[edit]Eventually, John invited Leo to a meeting under a false promise of peace, where the prince was captured. Leo and two of his sons, Roupen and Thoros, were subsequently taken prisoner.[5]
His last years in exile
[edit]Leo and his two sons were sent to prison in Constantinople. They were soon allowed to live in the court under surveillance and John acted more honorably towards Leo, with the two dining and going on hunting parties together. Leo's son Roupen was later murdered by Byzantine grandees that were envious of his strength.[5]
Leo died in Constantinople.[2]
Marriage and children
[edit]Orderic Vitalis states that Leo was "uncle to the wife of Bohemond II of Antioch". On this basis, some authors have proposed that Hugh I of Rethel or Gabriel of Melitene was her father.[citation needed]
- (?) unnamed daughter, who was the wife of a “Frankish knight from Antioch”, and mother of the Regent Thomas[citation needed]
- unnamed daughter, the wife of Vasil Dgha[citation needed]
- (?)[citation needed] Constantine[1] (? – Edessa, 1138/1144)[citation needed]
- Thoros II of Cilicia (? – February 6, 1169)[citation needed]
- Stephen (before 1110 – February 7, 1165)[citation needed]
- Mleh I of Cilicia (before 1120 – Sis, May 15, 1175)[citation needed]
- Roupen (after 1120 – Constantinople, 1141)[citation needed]
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ a b c d Runciman, Steven. A History of the Crusades – Volume II.: The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East: 1100–1187.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Ghazarian, Jacob G. The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393).
- ^ a b Kurkjian, Vahan M (1958). A History of Armenia. Armenian General Benevolent Union of America. p. 216. Retrieved 27 November 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Kurkjian 1958, pp. 219-220
- ^ a b c Bucossi, Alessandra; Suarez, Alex Rodriguez. John II Komnenos, Emperor of Byzantium: In the Shadow of Father and Son.
- ^ Vahram (2008-09-10). "Chronicle". Text Archive. Internet Archive. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ Kurkjian 1958, p. 220
Sources
[edit]- Bucossi, Alessandra; Suarez, Alex Rodriguez: John II Komnenos, Emperor of Byzantium: In the Shadow of Father and Son; Routledge, 2016, Abingdon; ISBN 978-1-4724-6024-0
- Ghazarian, Jacob G: The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393); RoutledgeCurzon (Taylor & Francis Group), 2000, Abingdon; ISBN 0-7007-1418-9
- Runciman, Steven (1952). A History of the Crusades, Volume II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
External links
[edit]- Smbat Sparapet's Chronicle
- The Barony of Cilician Armenia (Kurkjian's History of Armenia, Ch. 27)
